
14/07/2022 Know about cannabinoids, a group of compounds and an active element of the cannabis plant.
Although cannabis has been used for thousands of years, we are just now starting to comprehend the numerous chemical components that make up this multipurpose plant. While THC and CBD are presumably familiar to you, hundreds of additional cannabinoids interact with one another to have various physiological effects.
In the cannabis plant, there are compounds known as cannabinoids, and further, they interact with the body's Endocannabinoid System, which controls numerous physiological and mental functions. Cannabinoids come in a wide variety, and each has special qualities.
We'll discuss some of the most common cannabinoids' benefits, effects, and other aspects.
Cannabinoids: What Are They?
CBG reacts with the environment and changes into other cannabinoids like THC, CBD, THCV, and CBN when exposed to heat or light.
The cannabis plant produces dozens of naturally occurring chemicals called cannabinoids, including THCA, CBDA, and CBGA. The body's natural endocannabinoid system, a biological system based on chemicals that control several bodily functions, interacts with these cannabinoids. When you consume cannabis, cannabinoids bind to your Endocannabinoid System, causing feelings of euphoria, calmness, and other emotions.
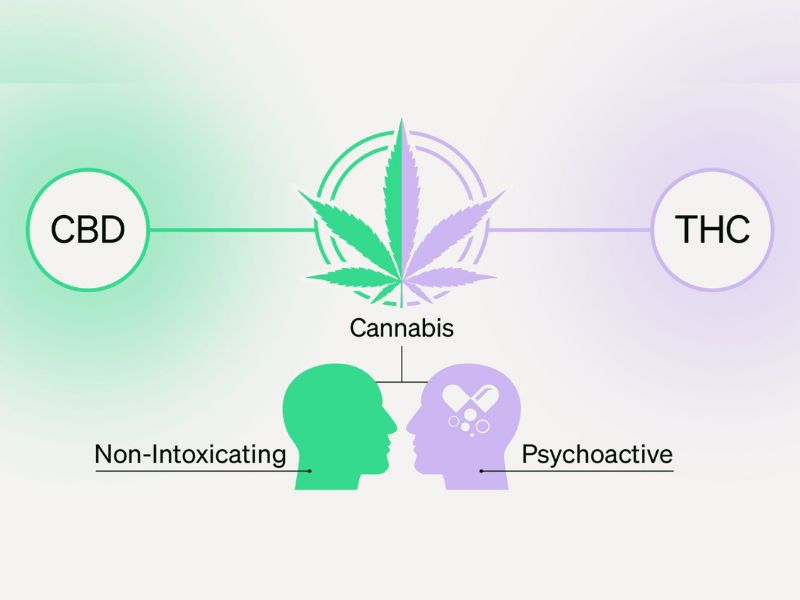
Source: Leafwell
How Do Cannabinoids Function in the Body?
The endocannabinoid system in our bodies and other receptors and ion channels interact with cannabinoids to produce various positive or negative effects. For instance, according to Dr. Kimless, "a small amount of THC can relieve nausea and vomiting, but too much THC might result in cannabis hyperemesis syndrome or persistent episodes of nausea and vomiting. Finding that balance for your own body is crucial.
Cannabis cannabinoids function by attaching to specific places on the nerves and in the brain. Although more than 100 cannabinoids exist in cannabis, THC and CBD have undergone the most research. The largest concentrations of cannabinoids are found in the plant's leaves and flowers.
Common Cannabinoids
You are already aware that THC and CBD are the cannabinoids that have received the most attention and research. However, more than 100 have been discovered in addition to other phytochemicals.
Following is a list of the most common cannabinoids and their effects:
THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol)
The most known cannabinoid is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is principally responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, or the "high." Its dominance over all others as the sole indicator of any given cannabis flower's caliber was once beginning to wane with the development of CBD.
The hippocampus, a region of the brain where memories are stored, can change how THC works. THC also affects the parts of the brain that are involved in pleasure, focus, movement, coordination, and time perception. Of all the cannabis active compounds, it is the most common. The arbitrary threshold that distinguishes a plant as cannabis from hemp is the presence of THC and precisely 0.3 percent THC.
Cannabidiol, or CBD
The second-most common cannabinoid present in cannabis is cannabidiol (CBD). This cannabinoid can lessen the negative consequences of becoming too high without making individuals feel "stoned" or drunk. Researchers and scientists are investigating using CBD to treat various conditions linked to inflammation, chronic pain, anxiety, and depression.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCv)
THCv is a cannabinoid that causes psychosis, but probably only at very high dosages. Additionally, it has been proposed that THCv suppresses hunger by obstructing a cannabinoid receptor.
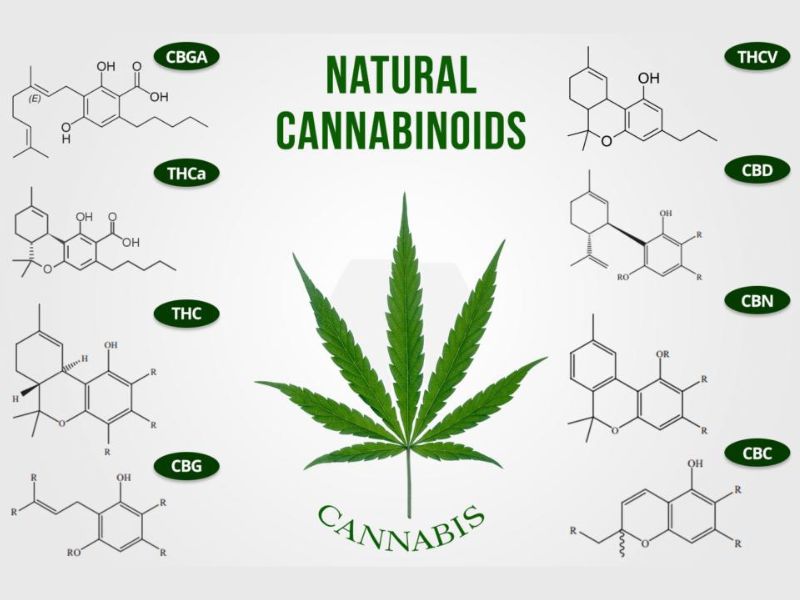
Source: Alive & Kicking
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA)
Since CBDA is the precursor to CBD, CBD cannot be produced until CBDA is first decarboxylated. This non-intoxicating cannabinoid is now being studied for several applications.
Cannabichromene (CBC)
After THC, CBC is the second most prevalent cannabinoid. However, it has no euphoric properties. Because it doesn't directly interact with CB1 receptors, this substance differs from the others. Instead, it interacts with the endocannabinoid system's less well-known TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors.
Cannabigerol, or CBG
Cannabigerol, the "mother" of all cannabinoids, is the foundation for developing THC and CBD. Enzymes convert the acidic form of CBG, CBGA, into THCA, CBDA, and CBCA as the plant ages (cannabichromene). Any CBDA still presents after this process turns into CBG when heated. The potential of CBG to treat conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, chronic pain, and epilepsy is drawing more and more attention.
Cannabinol (CBN)
As THC ages, it transforms into cannabinol (CBN). This cannabinoid works with THC to provide stronger sedative effects, making it effective for treating insomnia. CBN is most easily located in dried flowers.
Relations Among ECS
Depression and Memories
Although they can erase memories, cannabinoids can also help keep them intact. Cannabinoids' ability to affect mood suggests promise for treating anxiety and depression.
Appetite
Cannabinoids can enhance hunger, which is beneficial for nausea-causing disorders, but they can also lower appetite and treat conditions like diabetes.
Metabolism
The basic goal of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is to keep our bodies' internal environments stable. The ECS is essential in controlling metabolic risk factors linked to obesity in this way. Cannabinoids regulate several organs' glucose metabolism.
Reaction
An unfavorable reaction to stress stimuli can injure your body. ECS signaling may minimize stress and concern because cannabinoid receptors are strongly assembled in the hippocampus, a location linked to memory, learning, and emotional processes.
Immune Reaction
Cannabinoids modulate our immune system's response to infection and inflammation. Inhibiting cell signaling or causing cancer cells to die are two ways that endocannabinoid system modification hinders the growth of malignant cells.
Sleep
Cannabis has long been known to aid in sleep. According to studies, cannabinoids enhance sleep quality, reduce disruptions, and shorten the time needed to transition from being completely awake to sleeping.

Source: Pixabay
Do Cannabinoids Have Any Side Effects?
There are indeed side effects associated with cannabinoids. Depending on factors like weight, lifestyle, health status, and other details like current medications, the adverse effects will change from person to person.
Cannabinoids may have certain advantages, but there are also a lot of negative consequences associated with using the substance. This demonstrates how dangerous a natural drug addiction may be.
Among the side effects are:
~Rapid heartbeat
~Dizziness
~Depression
~Hallucination
~Low blood pressure
~Paranoia
~Panic attacks
~Food cravings
With the legalization and accessibility of cannabis expanding, the public's interest in cannabinoids is rising. Cannabinoids are a class of substances that resemble the chemical constituents of Cannabis sativa both physiologically and physically.
Since the time of Ancient China, these cannabinoids have existed. The Chinese employed them for several medical uses. Until 1937, when a federal law was issued outlawing the practice, using cannabis for medical reasons was also widely used in the United States.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids created and extracted from hemp plants are therefore lawful and available in various marketplaces. However, few states have legalized cannabinoids derived from marijuana plants, though this is changing. Currently, the District of Columbia and 30 states allow the use of cannabis for medicinal purposes. These medications are being prescribed by doctors more frequently for medical conditions like treating cancer patients' pain.
Some data suggest that CBD may aid in reducing pain perception. Researchers looked into hundreds of fibromyalgia patients in The Journal of Pain in 2021. Those who used CBD said it significantly or moderately reduced their discomfort.
Further, in a recent study, a group of male participants with high blood pressure was administered 600 mg of CBD daily for a few days to see how it affected their blood pressure. In the presence of CBD, men's blood pressure and heart rates during stressful tests are reduced.
Additionally, cannabis is a sophisticated plant that relies on the interactions of numerous chemical constituents to function. Cannabinoids are the original components of the cannabis plant's therapeutic properties, while terpenes, flavonoids, and cannasulfurs are also components we're learning more about.
Article by Ananya Bhattacharjee, Beverage Trade Network
TAGS:






